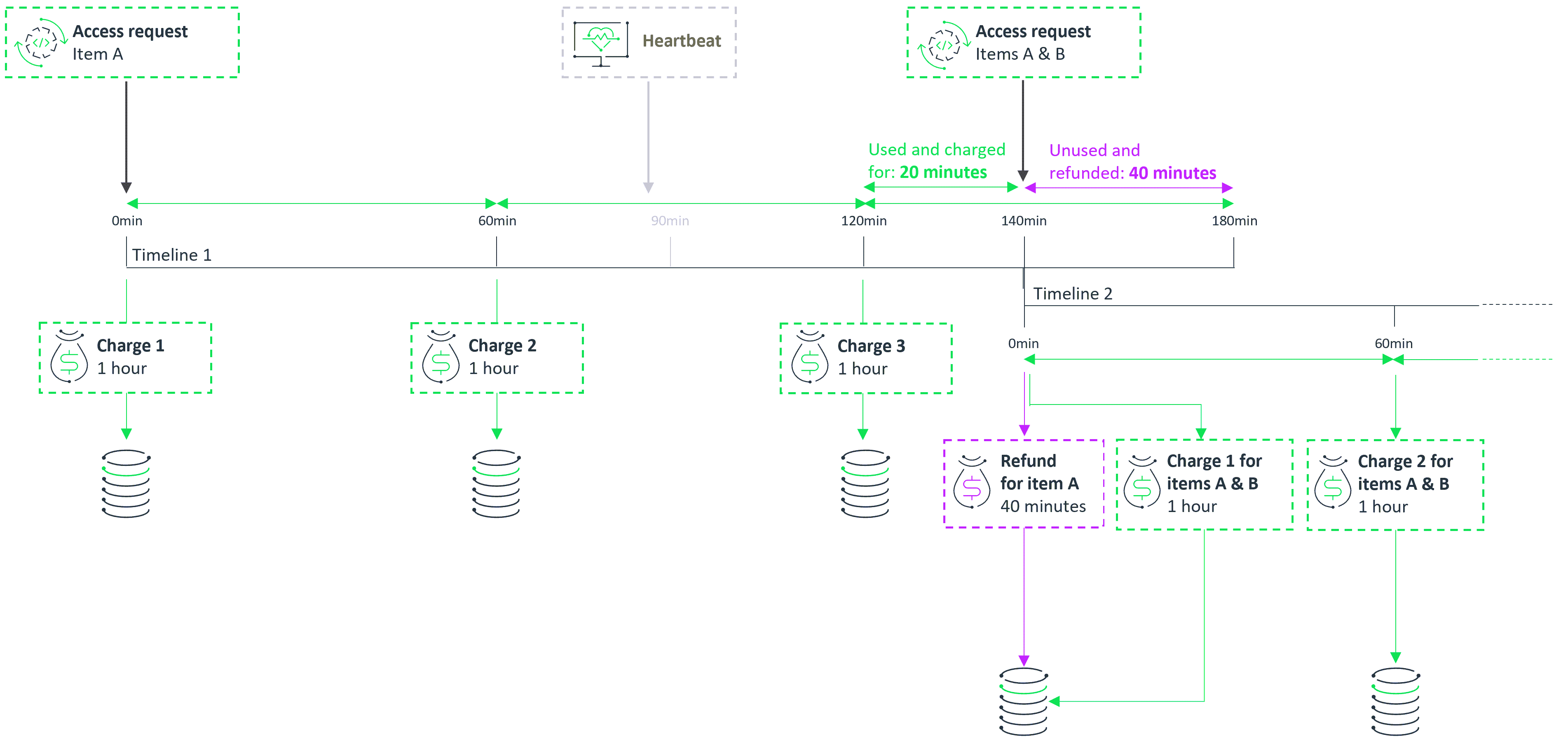
Scenario 2: Mid-session Charges
In this scenario, the client does not end the session between automatic charges. Instead, it requests an additional item—item B—twenty minutes after automatic charge 3.
This is the sequence of events:
| 1. | 0 minutes: Start of timeline. The client application requests item A. Elastic Access makes initial charge 1 and sends usage information to the data warehouse. |
| 2. | 60 minutes: Elastic Access makes automatic charge 2 and sends usage information to the data warehouse.´ |
| 3. | Between 60 and 120 minutes: Within 30 minutes of automatic charge 2, the client application sends a heartbeat to keep the session active. |
| 4. | 120 minutes: Elastic Access makes automatic charge 3 and sends usage information to the data warehouse. |
| 5. | 140 minutes: Twenty minutes after automatic charge 3, the client application wants to access item B in addition to item A. It therefore sends a regenerative access request for items A and item B. |
Elastic Access immediately calculates a refund for the unused time for item A (40 minutes), and calculates the new combined charge for item A and item B. If the new combined charge can be covered by the available tokens, Elastic Access does the following:
| • | Applies the refund and the new charge. |
| • | Starts a new timeline for automatic charges. |
| • | Sends relevant information to the data warehouse. |
This concludes the original timeline.
If the new charge cannot be successfully applied, Elastic Access will follow the course of action determined by the rollbackOnDeny field in the request (see also General Behavior for Session-Based Access Requests).