InstallShield 2016
Note • This section provides a description of virtualization in general for those that are not familiar with it. It does not represent the architecture of any specific vendor.
Virtualization enables you to isolate an application in its own environment so that it does not conflict with existing applications or modify the underlying operating system.
| • | Limitations of a Standard Installation Environment |
| • | Benefits of Application Virtualization |
Limitations of a Standard Installation Environment
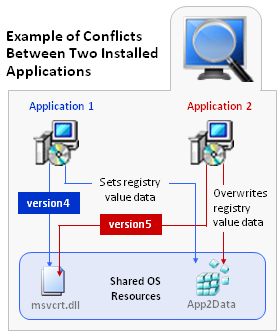
A typical Windows application has dependencies on components that are shared by multiple applications. Applications access these shared system resources, such as the registry or Windows system files. When an installation author recognizes that their application references a shared system component, they include a merge module to install that component.
When one of these shared components is installed, it is possible that a previously installed version of the same component could be overwritten; this may cause the existing application to break. A similar problem could occur when one of these applications containing a shared component is uninstalled. Because of these possible problems, extensive compatibility testing needs to be performed before an application can be distributed in the enterprise environment.
The following diagram provides an example of two conflicting installed applications.

Example of Conflicts Between Two Installed Applications
Benefits of Application Virtualization
Virtual applications run in virtual environments that keep the application layer and the operating system layer separate. Each application includes its own configuration information in its virtual environment. As a result, many applications can run side-by-side with other applications on the same computer without any conflicts.
Even though virtual applications are not installed on the local machine, they exhibit the same functionality and access to local services as locally installed applications, and also nearly the same performance characteristics.
The following diagram provides an example of how application virtualization would solve the conflicts that are shown in the previous example.
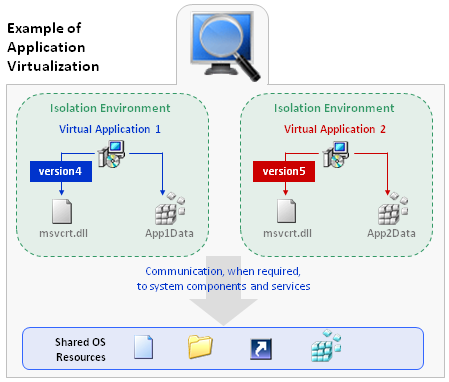
Example of Application Virtualization
Application virtualization allows the configuration of an application to be standardized to an isolation environment, rather than to an individual user’s desktop machine. Application objects, files, and registry settings are contained within this isolation environment. Critical application resources are managed locally by the isolation environment, thus minimizing resource dependencies between applications.
Application virtualization greatly reduces the scope for conflicts between applications and, therefore, simplifies compatibility testing.
See Also
Components of an App-V Package
Using the Microsoft App-V Assistant to Create an App-V Package
InstallShield 2016 Help LibraryMay 2017 |
Copyright Information | Flexera Software |